How can the guide help you?
There is a growing menace of cyber fraud, identity theft, economic offenses using online platforms, revenge porn, issues on online dating apps etc in the Internet era. For instance, one in every five internet users surveyed in India have faced online harassment.
It is important to understand which of the many instances of online abuse people can face in today’s day and age are crimes under the law, how we can enforce our rights in such cases and what the consequences of these actions can be.
What are the laws discussed in the guide?
- Indian Penal Code, 1860
- Information Technology Act, 2000
- Constitution of India
- Indecent Representation of Women (Prohibition) Act, 1986
Understanding the concept: Compromising Online Identity?
Impersonating another person on the internet, stealing pictures from social media profiles, cat-fishing and doxxing are some common examples of online identity theft.
What are my rights under the law against online identity theft?
• Protection of Right to Privacy – constitutionally guaranteed fundamental right under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution.
• Protection from ‘cheating by impersonation’ under the Indian Penal Code, 1860 (IPC)
• Protection against ‘online impersonation’ under the Information Technology Act, 2000 (IT Act)
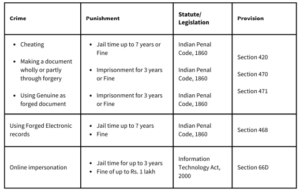
How does the law punish online identity theft?
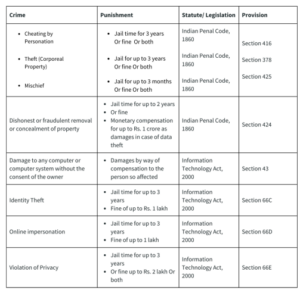
Understanding the concept: Cyber Bullying
Cyber-bullying is any act of intimidating or coercing another using an electronic means of communication. Sending unsolicited messages, black-mailing using private pictures, publishing nonconsensual pictures and videos (i.e. revenge porn), cyber-stalking etc are instances of cyber bullying.
What are my rights under the law against cyber bullying?
- Right to Privacy, a fundamental right guaranteed by the Indian Constitution
- Right to bodily integrity, an important aspect of Part III rights and safeguarded by the protective provisions in the Indian Penal Code 1860
- Right to be protected against offensive messages under the Information Technology Act, 2000
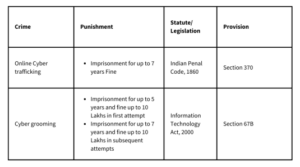
How does the law punish instances of cyber bullying?
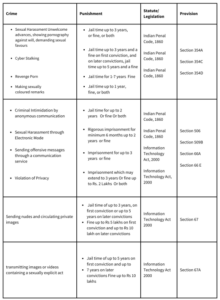
Understanding the concept: Online Financial Fraud
With growth of the internet and increasing interconnectedness, financial frauds have spilled over to the online world as well. From phishing scams over email to ‘Tinder swindlers’ on dating apps, fraudsters have widened their reach on the internet.
What are my rights under the law to protect me from online financial fraud?
- Legal right to be protected against the crime of cheating
- Right to approach appropriate authorities for redressal
How does the law punish those involved in online financial fraud?
MISCELLANEOUS :
Who can I complain to?
Process related information
Whom to approach?
You can approach the State Cyber cell or cyber crime cell of the city you reside in and file a complaint about the online abuse, harassment or financial scam you were a victim to. On receiving your complaint, they will start the investigation on your behalf and initiate the criminal justice system.
Online Crime Reporting Portal maintained by the Ministry of Home Affairs is another option to lodge your complaint.
Alternatively, you can approach your local police station and file an FIR enumerating details of the complaint. Another option to file a private complaint with the judicial magistrate of the region you reside in.
Types of authorities and their work
State and District Level Cyber Cells
Cyber cells investigate and look into cases of online crimes. They assist the State police forces in their investigation and provide electronic evidence required during the trial. On filing your complaint, they will initiate the criminal justice process on your behalf.
Ministry of Home Affairs’ National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal
On visiting the portal (https://cybercrime.gov.in/Default.aspx), you will be redirected to a specific State Government’s website to register a complaint. In the section “Services for Citizen”, click on “Report a Cyber Crime. Choose from ‘Report Cyber Crime Related to Women/Child’ or ‘Report Other Cyber Crime’. Here, you can provide information about the offender, the victim, and the incident along with any supporting evidence, such as screenshots.
If you have created an account, there is an option for you to track the status of the investigation after you have filed the complaint.
You can find state specific information on reporting a cyber crime here.
Local Police Station
The easiest way to report the cyber crime is to approach your local police station and file an FIR. Provide complete details of the crime you have fallen victim to. On filing an FIR, the criminal process is set in motion.
The Information Technology Act has stated that any cyber crime has a global jurisdiction. Due to this, a cyber crime complaint can be filed at any cyber cell/police station situated in your city or elsewhere. But, it is advisable to always approach a cyber cell that is closer to your place for better access.
Approaching your local judicial magistrate
If you are unable to file a FIR at the police station or if you want to lodge a private complaint, you can approach the judicial magistrate of the area you reside in and lodge a private complaint either orally or in writing. The Magistrate will decide on further course of action and investigation after hearing the complaint.
SPOTLIGHT: Cybercrime Incident Reporting System in Bengaluru
The Bengaluru City Police has set up ‘Cybercrime Incident Reporting System’ wherein citizens can lodge their complaint 24×7 by dialing 112.
This enables filing of ‘Cyber Information Report’ (CIR) before filing a ‘First Information Report’ (FIR). This helps reduce the time gap between commission of the offense and reporting the offence, enabling a move towards a ‘victim oriented approach’.
Key Features:
- Expedite the process of cybercrime investigation
- Reduced response time to online fraud
- Trained personnel to handle online crimes
- Victim well being given priority over procedural requirements
SPOTLIGHT: National Cybercrime Reporting Portal, Ministry of Home Affairs – applicable to all districts in Karnataka, except Bengaluru
This portal, set up by the Central Government can be accessed from 10 am to 6 pm by dialing 1930 for reporting cyber financial frauds.
The procedure followed are as follows:
- On receiving the complaint, details are immediately entered on the portal and shared with the concerned bank simultaneously. This helps in stopping fund transfer to the fraudster’s account.
- The user filing the complaint receives a SMS link for accessing the portal and filing in further details.
- This is sent to the concerned police station where the FIR is filed.
Key features:
- The portal is handled by the Criminal Investigation Department (CID) in Karnataka
- Eases process of lodging complaints
- Can deter transactions if informed to the portal within two hours of the cybercrime
SPOTLIGHT: Police Didi Initiative by Mumbai Police
The Mumbai Police had initiated the ‘Police Didi’ campaign in 2016 to educate adolescent school children, particularly girl students about the hidden dangers in the cyberworld. Around 200 women police officers were specifically trained by cyber experts, child counselors and psychiatrists to help children. Their mandate includes visiting schools, chawls, residential societies, slums, colleges etc and engaging in conversations with children. If incidents of cyber crime are discovered, they would help initiate legal action and approach the authorities. This initiative reinforces the concept of ‘good friend’ and ‘bad friend’ in online portals.
SPOTLIGHT: National Commission for Women’s ‘Digital Literacy Programme’
The National Commission for Women launched the ‘Digital Literacy Program’ in 2018, in collaboration with Facebook and CyberPeace Foundation, for educating college or university girl students about cybercrimes and ways to tackle them. It focuses on promoting digital literacy for women including the precautions that can be taken; raising awareness about cyber crimes; and advising the users about the resources available to women; to prevent the problems and also how to handle such crimes. The programme, in its initial phase, covers the states of Punjab, Manipur, Haryana, Meghalaya, Delhi-NCR, Sikkim, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
Resources
Support Systems in Bengaluru
Legal Aid Systems
1. National Legal Services Authority: 011-23385321
2. National Legal Helpline- 15100
3. Childline: 1098
4. Karnataka State Legal Services Authority:
• Helpline- 1800-425-90900
• Phone Number- 080-22111714, 080-22111729
• District legal services list
5. Women’s Police Station, Bengaluru: 080 2294 3250
• Find the document with contact numbers of different stations here.
6. Women Cyber Security Cell: 099000 39039
7. Bangalore Police Headquarters: 080 2294 2595
8. Karnataka State Commission for Women: 080- 22216485/486 Fax: 080-22216485
Helplines
1. National Commission for Women Helpline Number: 181
2. Women in Distress helpline number: 1091
3. Karnataka State Human Rights Commission: 080 2239 2203
4. Central Social Welfare Board -Police Helpline: 1091/ 1291; (011) 23317004
5. Women’s And Children’s Safety Help Line: 09108445555
6. Ask SHEROES: Find the online chatting service here.
Support Systems in Delhi
Legal Authorities
1. Delhi State Legal Services Authority:
• Helpline- 1516
• Phone Number- +91 96679 92802
• Mobile Application- Vidhik Sewa
2. National Legal Services Authority:
• National Legal Helpline-15100
3. Women’s Cell Delhi Police: Find the document with contact numbers of different stations here.
4. Delhi Commission for Women: (011) 23379181/ 23370597
5. Child-line: 1098
Helplines
1. National Commission for Women Helpline Number: 181
2. Women in Distress helpline number: 1091
3. Central Social Welfare Board -Police Helpline: 1091/ 1291;
4. Ask SHEROES: Find the online chatting service here.
Other resources
1. List of cyber cell police stations in Delhi – http://www.cybercelldelhi.in/districtcybercell.html
Support Systems in Mumbai
Legal Authorities
1. National Legal Services Authority: National Legal Helpline- 1516
2. Maharashtra State Legal Services Authority:
Toll free Helpline Number:1800 22 23 24;
Tel.: 022-22691395
District Legal Services List
3. Contact numbers of different stations list
• Mumbai Cyber Station- +022 26504008
• Mumbai Police Women Helpline- +022 22633333, 103
4. Maharashtra State Commission for Women: Helpline- 155209; Contact No.- +022 26592707
Helplines
1. National Commission for Women Helpline Number: 181
2. Women in Distress helpline number: 1091
3. Central Social Welfare Board -Police Helpline: 1091/ 1291; (011) 23317004
4. Maharashtra State Human Rights Commission: +022 22092857
5. Ask SHEROES: Find the online chatting service here.
Here is a list of Nodal Officers of various internet service providers that you can write to, to report a complaint.
[Insert table here]
Let us test your knowledge:
Answers in Yes/No
1. Can I report someone who has created a fake Instagram account using my photos and sends lewd messages to all my friends? (Yes/No)
2. My private pictures which I had sent my ex-boyfriend are now being circulated on social media platforms without my knowledge or consent after our break up. Can I sue him? (Yes/No)
3. Someone has just defrauded me by claiming he is from the bank. Can the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal help me in getting my money back if I lodge a complaint at the earliest? (Yes/No)
4. Can I file an ‘anonymous complaint’ on the Ministry of Home Affairs’ Online Crime Reporting Portal? (Yes/No)
5. Someone I met on a dating app is stalking me on all my social media platforms, can he be brought before the law? (Yes/No)
6. Can I lodge a complaint against someone who has been sending me unsolicited messages on Instagram? (Yes/No)
7. I have been defrauded by someone on the internet who offered me 20% returns for investing Rs. 10 lakhs. He claimed he is from the RBI and showed me papers to reinforce his statements. However, later I realized that I have been duped. Can I lodge a complaint against him for theft, cheating and forgery? (Yes/No)
8. I am a social media influencer. I have public social media pages where people at times comment inappropriately and send me vulgar messages via personal chat. Can I initiate legal action against the offenders? (Yes/No)
9. Someone has stolen sensitive information from my laptop, including private pictures, when I gave my laptop for repair. Am I eligible to get compensation for the loss suffered? (Yes/No)
10. Someone has shared private information about my sexuality via social media handles tagging me publicly, can I file a complaint against him? (Yes/No)