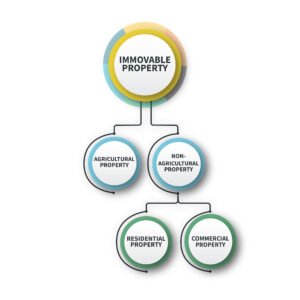
Under Indian laws, immovable property includes land, buildings, hereditary allowances, rights to ways, lights, ferries, fisheries or any other benefit to arise out of land, and things attached to the earth, or permanently fastened to anything which is attached to the earth, but not standing timber, growing crops nor grass.(( Section 2 (6) of the Registration Act, 1908)) Due to the fact that land is a state subject under Schedule VII of the Indian constitution, the laws governing immovable property vary from state to state.

Green city Developers
January 20, 2026
This explainer is very informative for anyone trying to understand the different types of immovable property and their legal definitions. It breaks down categories clearly and helps clarify important terms you should know before buying or investing.